Things you may not know about water in the body
Have you ever wondered how much water is in your body? Let's explore some things you may not know about water in the body with Karofi in the following article.
1. Water in the body varies based on individual factors
The amount of water in the human body ranges from 50-75%.
Infants and newborns have the highest water percentage with 75% in newborns and decreasing to 65% in 1-year-old children.
In an adult human, the average water rate in the body is composed of 50-65% water. Adult women have a lower water percentage than adult men.
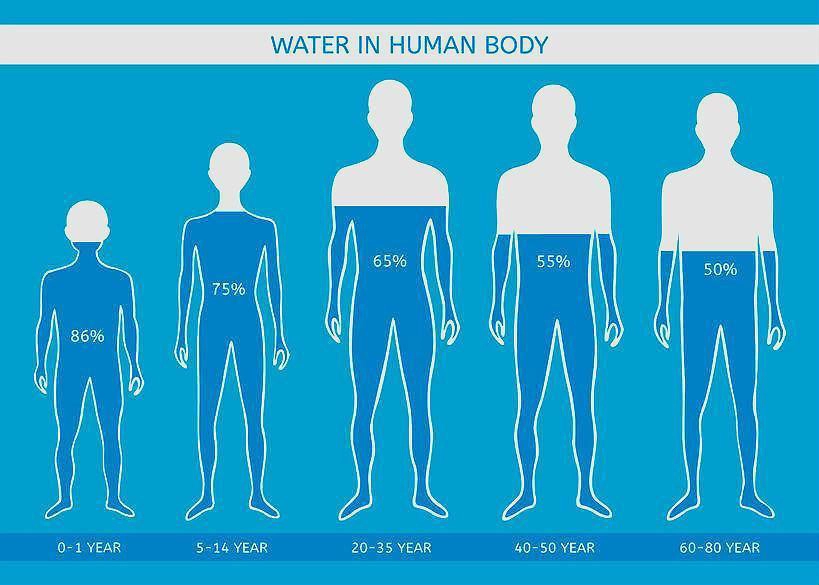
Obese individuals will have a lower water percentage than thin people.
The percentage of water content depends on the remaining water balance in your body. You will feel thirsty when you have lost about 2-3% of the water in your body.
2. What is the function of water in the body?
Water acts as a regulator of the internal body temperature. This is partly due to water having a high specific heat. The body uses sweat to regulate temperature. Water is necessary for the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates, and is a major component of saliva, aiding in food swallowing.
Water lubricates joints and acts as a shock absorber. Water is also used to excrete and eliminate toxins from the body through urine. Water dissolves minerals, soluble vitamins, and some nutrients. Water also transports oxygen and nutrients to cells.
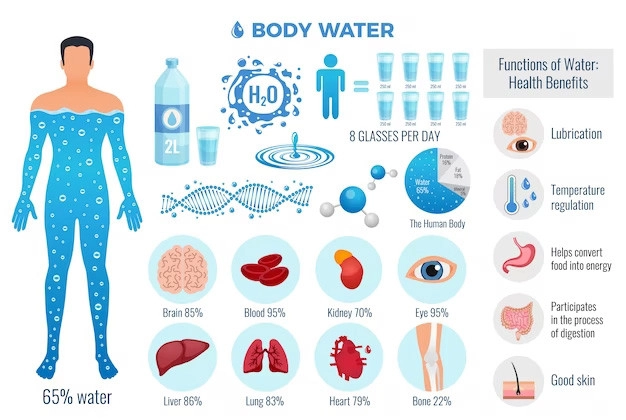
The water we drink is absorbed by the gut and circulated throughout the body. Water performs various functions and is then excreted through urine. When the body temperature increases, blood circulation to the skin increases. Then, the body sweats, helping to balance body temperature.
3. Where is water located in the human body?
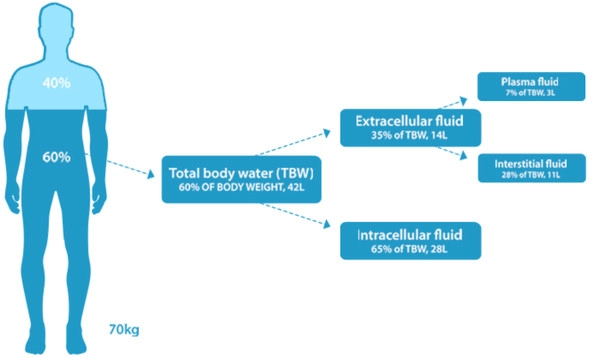
The total amount of water in our body is mainly found in three locations: within our cells (about two-thirds of the water), in the space between cells and in our blood (one-third of the water).
The more muscular our body, the more water it contains. Conversely, the more body fat, the less water it contains, as fat in the body has less water.
4. The journey of water through the human body
One of the main differences between food and water intake is that while food is absorbed through digestion, water is absorbed into the body's organs.
4.1 The first step of water's journey starts from the mouth
The first major step is water passing through the mouth. After a few sips of water, the brain signals to the body that it has been adequately hydrated.
This is an important mechanism because it takes a long time for water to be delivered to the cells. If the brain only signaled after the cells received water, people would drink more water than their actual needs.
The communication between the brain and the mouth allows someone to stop drinking at the appropriate time, even if the body hasn't fully absorbed enough water yet.
4.2 Water passes through your esophagus
The esophagus is a small tube connected to the mouth and goes down to the stomach. This is where the process of water absorption into the blood begins.
4.3 Water and your stomach
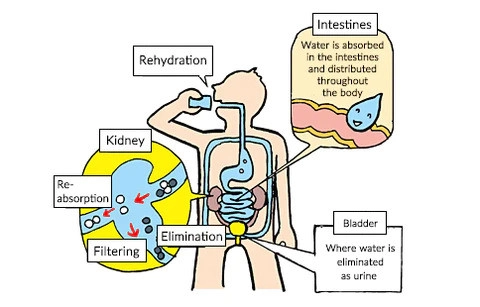
The amount of water absorbed in the stomach and how quickly it is absorbed, in part, depends on the amount of food that has been consumed. If you drink water on an empty stomach, the rate of water absorption will be faster. Meanwhile, if someone has eaten a lot of food before drinking water, the absorption rate will slow down, and the process can take up to several hours.
4.4 Water and your small intestines
The small intestine, about 6.5m long, effectively absorbs water into cell membranes and blood. From here, water will move to cells throughout the body to efficiently perform everyday bodily functions.
4.5 Water and your large intestines
The large intestines are the important center for absorbing water and electrolytes, rather than the stomach and small intestines.
4.6 Water and Your Kidneys
The kidneys act as a detox filter, but to efficiently flush toxins, they require a large amount of water. If the kidneys do not receive enough water, it can lead to health concerns such as kidney stones and other kidney-related diseases.
Fortunately, there is a way that the kidneys communicate with us about whether our bodies are adequately hydrated or not, by observing the change in the color of urine from light yellow to dark yellow.
Although our kidneys help filter out harmful toxins in our bodies, there is another way to help you maintain safe and clean drinking water. With home water filtration systems, water treatment devices such as hot and cold water purifiers, drinking water is ensured with the removal of up to 99.99% of harmful pollutants that may affect your health.
4.7 Water and Your Brain
Water is also sent to the brain to provide water to brain cells. Here, water is used to maintain certain brain functions. If not properly hydrated, studies have shown that people may experience decreased short-term memory function and visual motor skills.
Through this article, you can see the importance of water in the body, so providing adequate water to the body is truly necessary. However, in addition to that, you should also pay special attention to the quality of drinking water, especially in the current complex situation of water source pollution. To protect the health of many families, many people have chosen to use home water filtration systems or hot and cold water purifiers, which are capable of removing up to 99.9% of impurities and providing pure drinking water with a variety of demands. If you are looking for advice on Karofi's product lines, please contact us via WhatsApp +84837748966 or visit Karofiglobal.com/en for free and fastest consultation.